Matter, the stuff from which our physical world is formed, presents to us as various types of material. On a first analysis, the possible phases are:
-gaseous, such as air
-liquid, such as water
-solid, such as rock
However, for classification purposes it is useful to divide materials into:
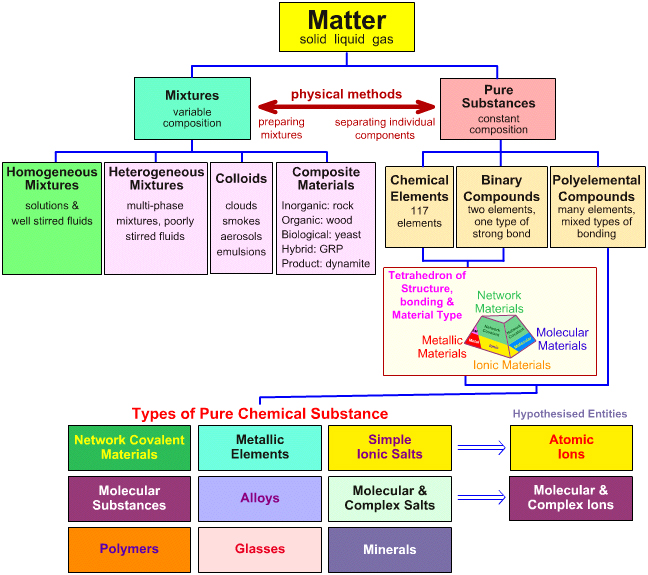
Here is the chart of matter:
- mixtures: variable composition
- pure substances: stoichiometric composition
There are 2 kinds of changes
1. Physical change
2. Chemical change
What are the differences between these two?
A physical change is a change in which no new substance is formed, for example, freezing water into ice just results in water molecules which are 'stuck' together - it's still H2O;
 |
| ice melting |
A chemical change results in the formation of one or more new substances, for example,burning wood results in ash, carbon dioxide, etc, all new substances which weren't there when you started.
 |
| wood burning |
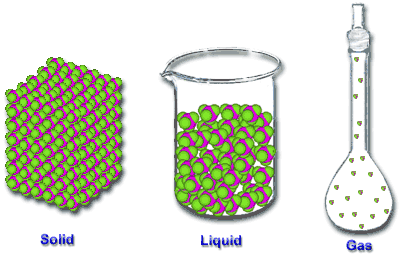
Solid - the particles (ions, atoms or molecules) are packed closely together. The forces between particles are strong enough so that the particles cannot move freely but can only vibrate. As a result, a solid has a stable, definite shape, and a definite volume. Solids can only change their shape by force, as when broken or cut.
Liquid - it is a nearly incompressible fluid which is able to conform to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. The volume is definite if the temperature and pressure are constant.
Gas - it is a compressible fluid. Not only will a gas conform to the shape of its container but it will also expand to fill the container.